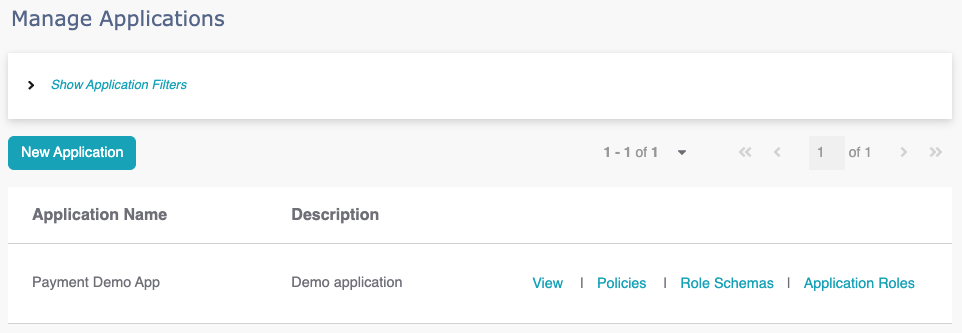
Manage Applications
Manage Role Schemas
The application role schema defines the data model and UI for
application roles, including membership attributes. Application
roles are created from the schema, with the "Default" schema
containing role names only
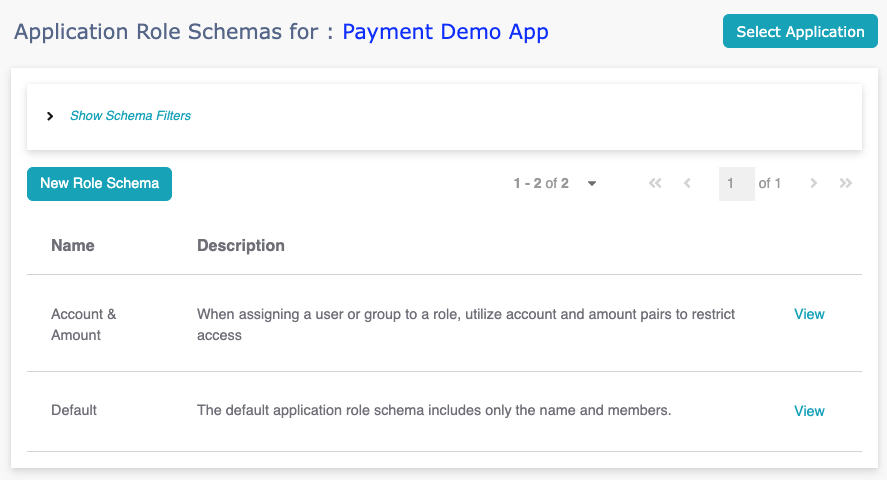
To set up the application role schema, you must first select an
application and use the "Select Application" button to designate
the "current" application.
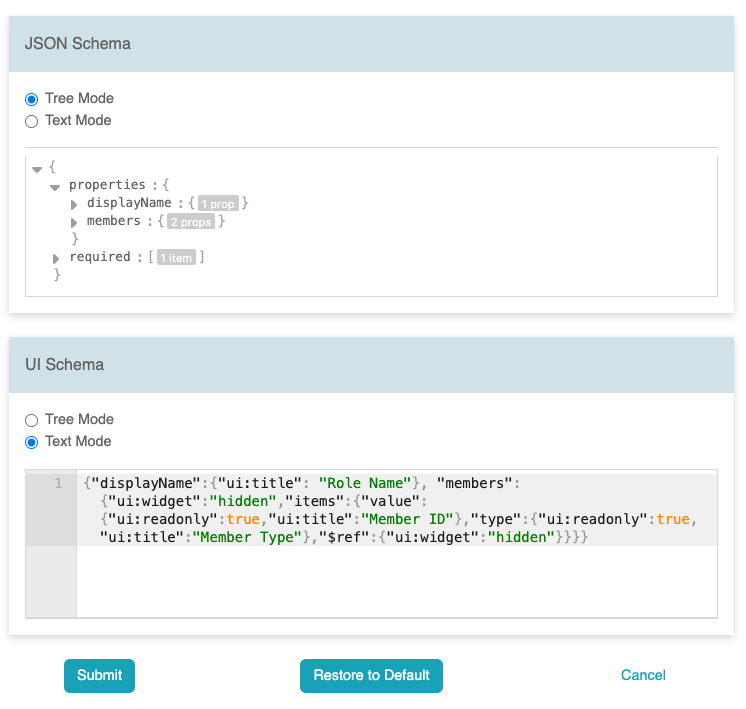
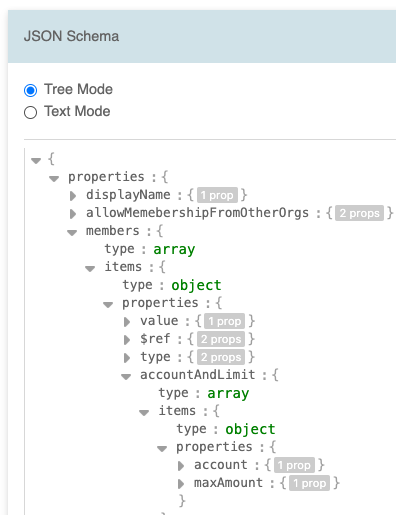
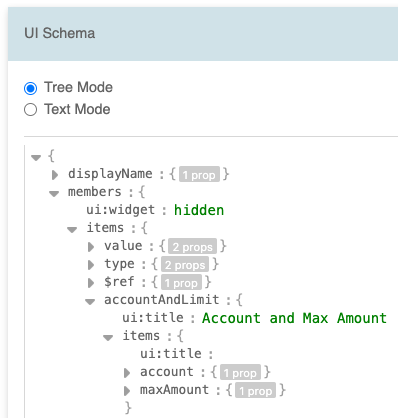
The JSON and UI schema editor supports both tree mode, ideal for
modifying schema, and text mode for copy/paste operations.
For additional information on JSON schema details, please refer to
json-schema.org.
Likewise, for UI schema details, you can visit
rjsf-team.github.io/react-jsonschema-form/docs/api-reference/uiSchema
To test the schema, you can use this playground:
https://rjsf-team.github.io/react-jsonschema-form/
Manage Application Roles
To manage application roles, you must first select an application.
On the "Application Roles" page, use the "Select Application"
button to designate the "current" application.
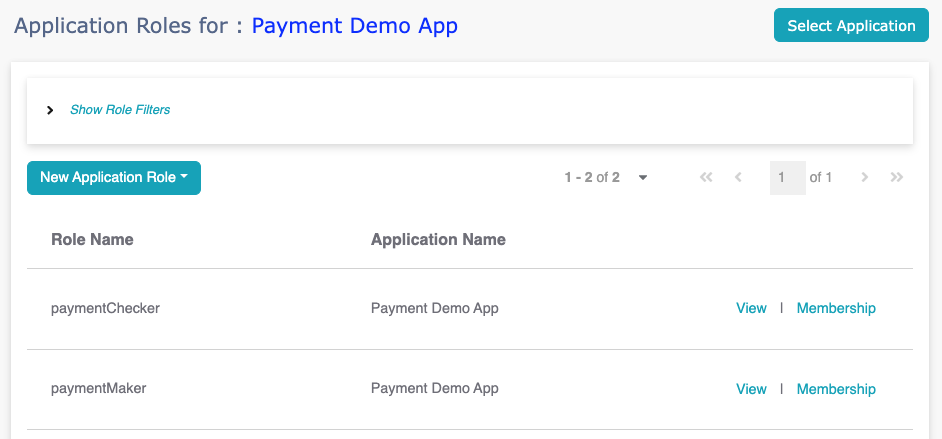
When multiple schemas exist for an application, you must first
select a role schema before creating application roles.
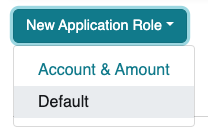
Provide the role name and all the schema-defined attributes when
creating a role.
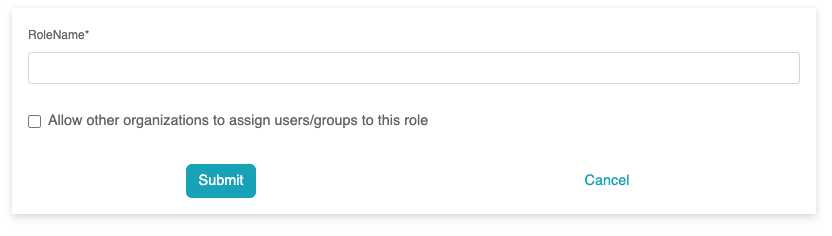
When deleting a role, ensure the role is not referenced in any SoD
policy to avoid deletion failure.
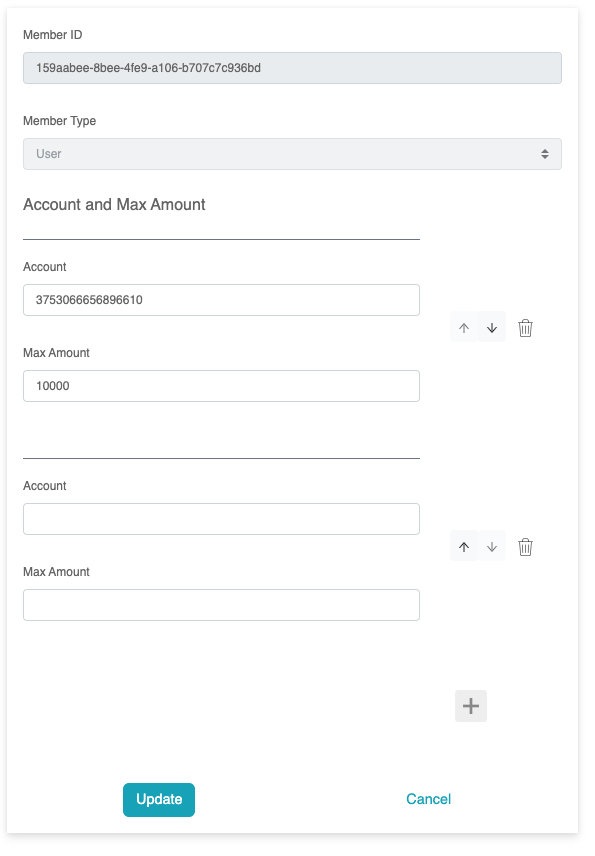
Note that the account and amount attributes are not for the role
itself but for membership. For instance, when a user is assigned
to the paymentChecker role, they are allowed to use account #1
with a maximum amount of $5000.
It's also possible to define the schema and include the account
and amount on the role itself, although it represents a different
model.
Application role membership management is combined with global
role management. To manage role membership, click the "membership"
link for the role, or click "Role" -> "Role Membership" in the
left panel.
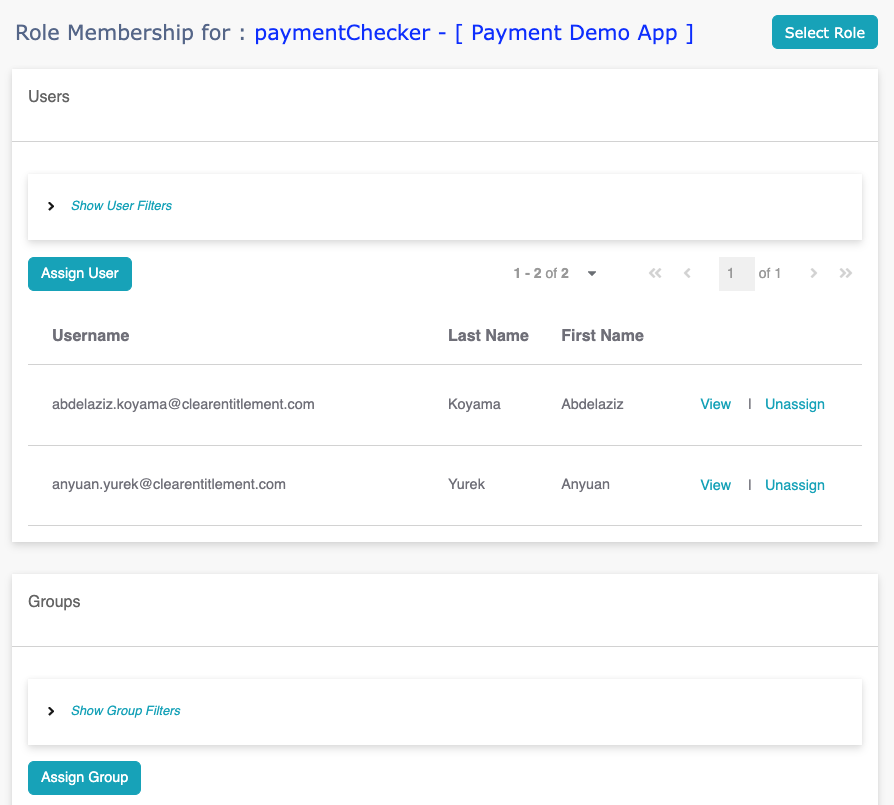
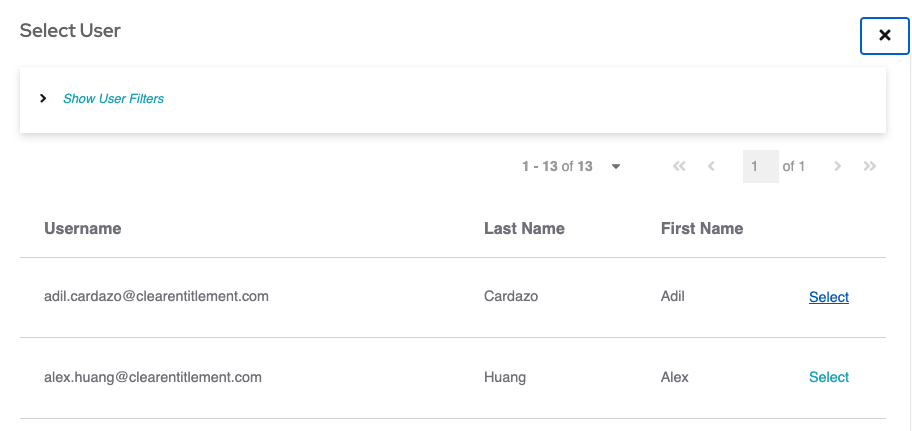
To assign membership, click "Assign User" or "Assign Group", then
select the user/group and fill in the membership attributes.
Manage Application Policies
For policy model and management workflow information, please visit
the
POLICY GUIDE
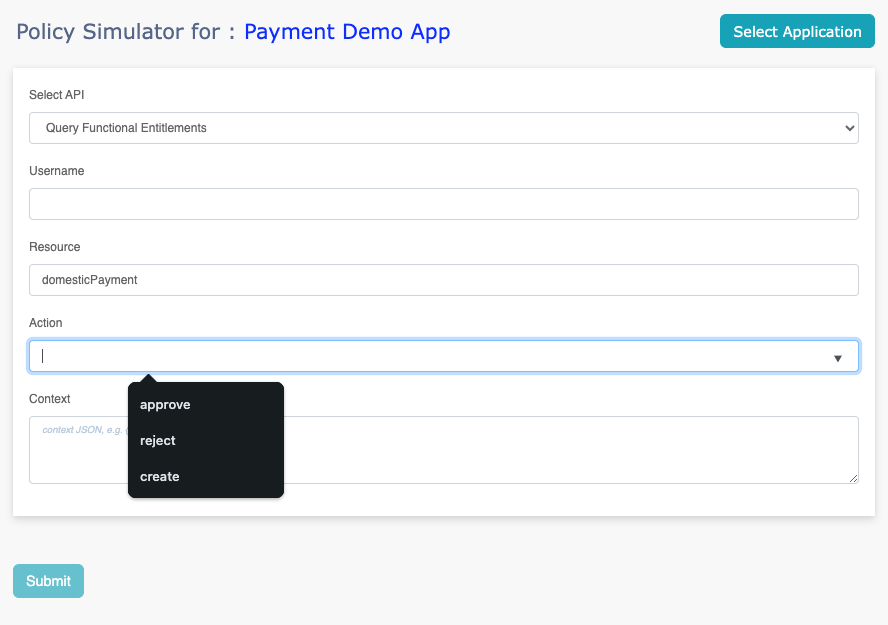
Policy Simulator
Use the simulator to test deployed policies. Once the application
is selected, the resource and action are pre-populated with
candidate resources and actions defined in the policy.
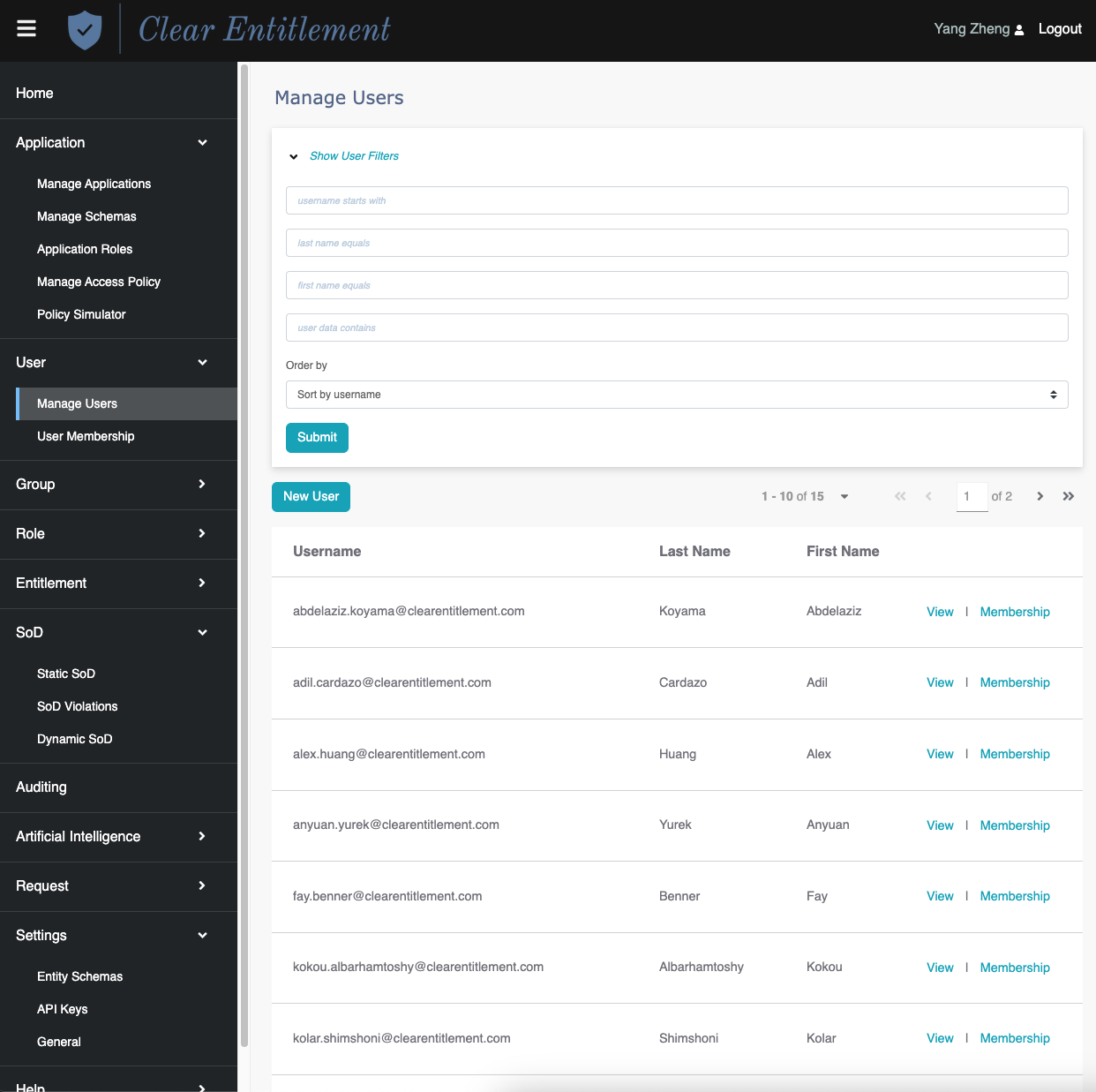
Manage Users
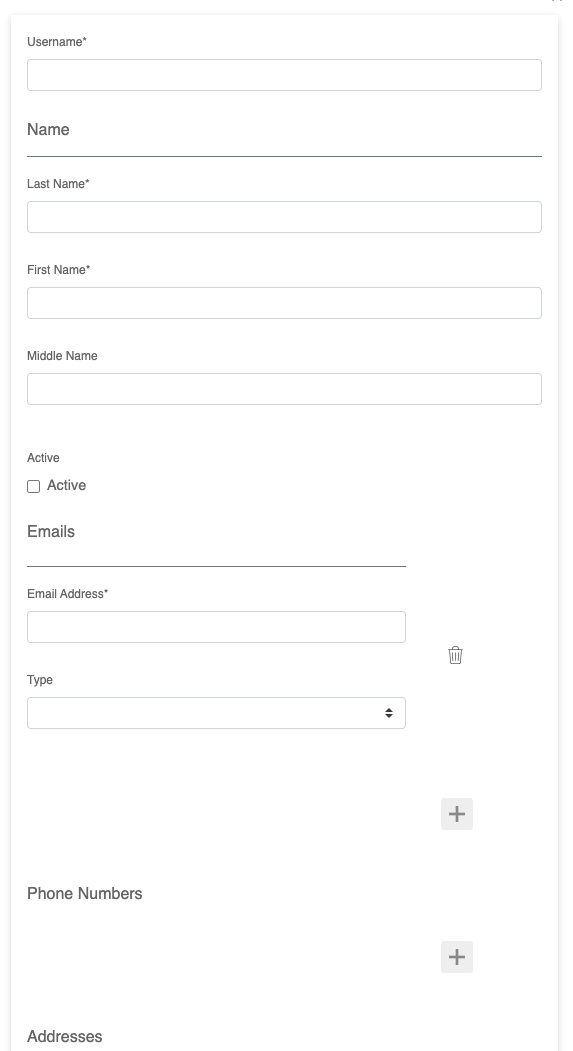
The default user schema displays limited user attributes such as
username, last name, first name, emails, and phones. To customize
the user schema, navigate to "Settings" -> "Entity Schemas" and
update the user's JSON and UI schema.
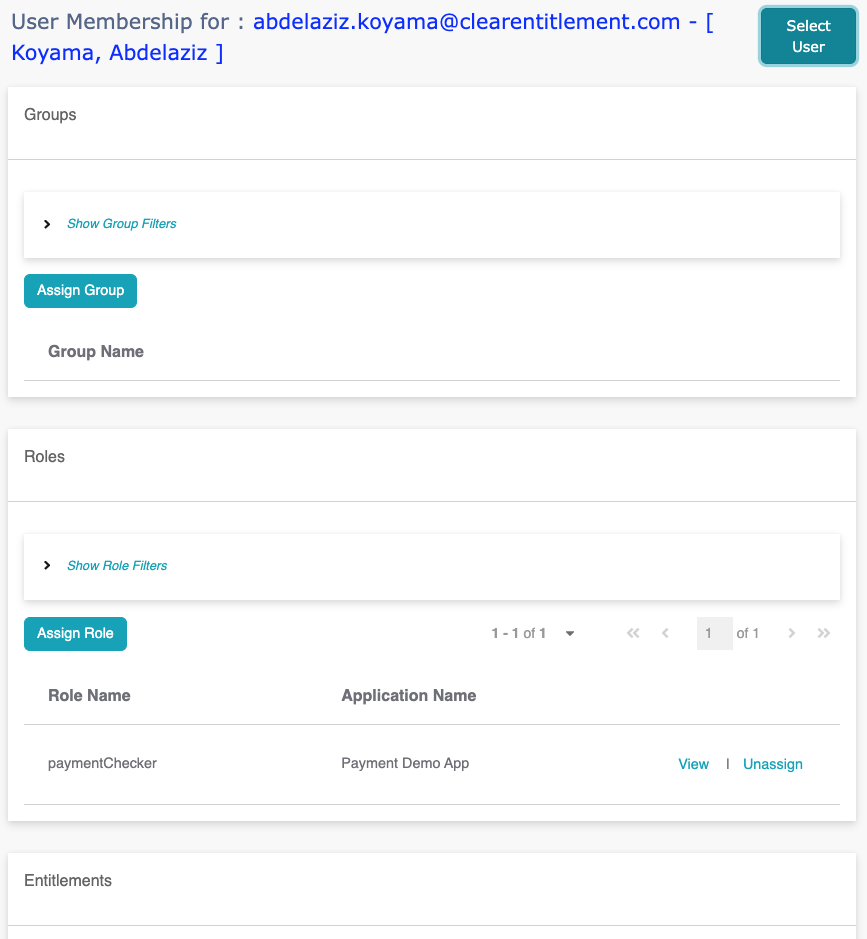
User Membership
Membership can be managed from both parent and child sides. For
example, you can choose a role and manage its children or start
from a user and manage its groups and roles.
Manage Groups
The default group schema displays the group name only. To
customize the group schema, navigate to "Settings" -> "Entity
Schemas" and update the group's JSON and UI schema.
Group Membership
Membership can be managed from both parent and child sides. For
example, you can choose a group and manage its children or start
from a user and manage its groups and roles.
Manage Role
The default role schema displays the role name only. To customize
the role schema, navigate to "Settings" -> "Entity Schemas" and
update the role's JSON and UI schema.
Role Membership
Membership can be managed from both parent and child sides. For
example, you can choose a role and manage its children or start
from a user and manage its groups and roles.
Manage Entitlements
Clear Entitlement utilizes the entitlement entity to conveniently
group attributes. For instance, in the payment demo app, when
dealing with a large number of accounts, it may be easier to
classify them into groups for provisioning account access. For
details, refer to the policy models in the
POLICY GUIDE
The default entitlement schema displays the entitlement name only.
To customize the entitlement schema, navigate to "Settings" ->
"Entity Schemas" and update the entitlement's JSON and UI schema.
Entitlement Membership
Membership can be managed from both parent and child sides. For
instance, you can choose an entitlement and manage its children or
start from a user and manage its groups and roles.
Note that entitlement can have a user or role as a child.
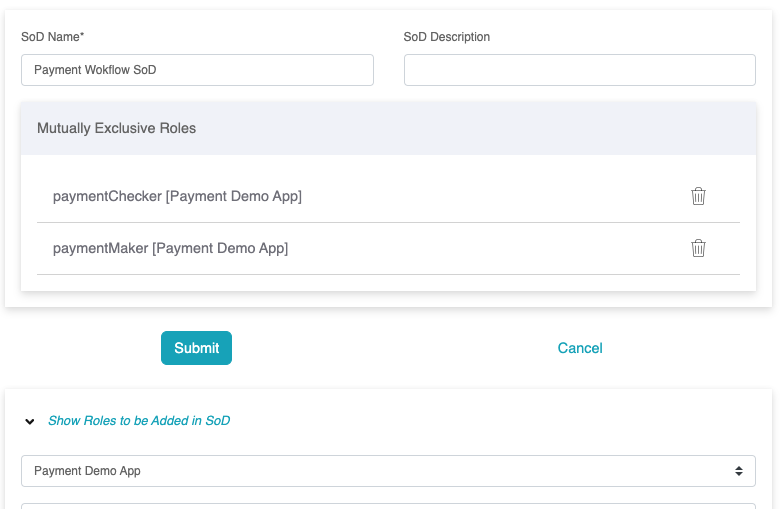
Static SoD
Static SoD refers to a mutually exclusive set of roles where a
user can only be assigned to at most one role in the SoD, either
directly or through group membership.
SoD Violations
Violations are typically prevented, but they may exist before SoD
rules are created. Additionally, group membership may be handled
outside of Clear Entitlement, such as in Active Directory, making
it impossible to prevent all violations.
Auditing tables display the history of data changes.
API Keys
API Key support is available but not encouraged; access tokens are
preferred.
The API client assumes the privileges of the API
key owner.